CPU undervolting adjusts the CPU’s power supply to enhance efficiency and reduce electricity use. This process saves energy, lowers heat, and maintains computer performance.
How Undervolting Works
Undervolting adjusts the CPU’s voltage settings to provide optimal power, avoiding excessive heat and power consumption. This is done by incrementally lowering the voltage while monitoring the CPU’s stability and performance.
Undervolting involves altering factory settings, which carries risks. It should only be performed by those with sufficient technical knowledge and understanding of the potential consequences, including the risk of damaging the hardware.Caution
Process of Undervolting
- Installation: Begin undervolting by downloading and installing software such as ‘intel-undervolt’ from online repositories.
- Configuration: Check your CPU’s current power usage by reviewing its voltage settings. Adjust these in the configuration file on your computer.
- Testing and Adjustment: Test for stability after configuring, making iterative adjustments to find the optimal configuration.
- Persistence: Enable services like intel-undervolt.service to maintain these changes.
Steps for Successful Undervolting
Step 1: Benchmarking
Before making any changes, run a baseline performance test using software like Cinebench or 3DMark. This will help you compare the system’s performance before and after undervolting.
Step 2: Gradual Adjustments
Start by slightly lowering the voltage. A common approach is to reduce the voltage in small increments (e.g., 0.01V at a time) and test for stability after each adjustment.
Step 3: Stability Testing
Use programs like Prime95 or AIDA64, which are like intense workout routines for your computer, to check if it remains stable and doesn’t crash under pressure after the voltage changes.
Step 4: Monitoring
Continuously monitor the system’s temperature and performance using Camomile, HWMonitor, or a similar tool. Look for any unusual behavior or temperature spikes.
Step 5: Finding the Sweet Spot
The aim is to find the perfect balance where your CPU uses the least amount of power possible without slowing down your computer. This is like finding the ‘sweet spot’ where it works efficiently but stays cool. This optimal point varies for each CPU/GPU.
Benefits of Undervolting a CPU
Energy Efficiency and Heat Reduction: Undervolting significantly reduces heat, which is beneficial for laptops and compact PCs, leading to lower energy consumption and extended battery life.
Performance Stability and Longevity: Lower operating temperatures from undervolting prevent CPU throttling under heavy loads, ensuring stable performance and potentially extending CPU and component lifespan by reducing thermal stress.
Tips for Successful Undervolting
- Backup Data: Always backup important data before making system changes.
- Avoid Drastic Changes: Make small voltage adjustments to avoid system instability.
- Keep an Eye on Temperatures: Monitor temperatures closely, especially during stress testing.
- Research Your Specific Hardware: Different CPUs and GPUs have different tolerances. Research community experiences with similar hardware.
Risks Associated with Undervolting
Potential for Instability and Crashes
If the voltage is set too low, the CPU might not receive enough power to operate correctly, leading to system instability, crashes, or even failure to boot.
Possible Impacts on Warranty and Support
It is important to note that undervolting might void the manufacturer’s warranty or lead to unsupported configurations. Always check with your device manufacturer for warranty and support information before proceeding.
Difference Between Undervolting, Underclocking, and Overclocking
While undervolting focuses on reducing voltage, underclocking involves lowering the CPU’s clock speed, thereby reducing its power consumption and heat output. Overclocking, on the other hand, increases the clock speed beyond the manufacturer’s specifications to boost performance, often requiring increased voltage and better cooling solutions.
Undervolting in Different CPU Models
- Intel CPUs: Procedures and recommendations for undervolting Intel CPUs vary based on the specific model and generation. Users must follow guidelines specific to their CPU type.
- AMD CPUs: Compatibility and limitations differ for AMD CPUs, with some models offering less flexibility for undervolting compared to Intel CPUs.
Practical Tips for Successful Undervolting
- Starting with Conservative Settings: Begin with small voltage reductions and gradually adjust while monitoring stability and temperatures.
- Monitoring CPU Temperatures and Performance: Use software tools to track the CPU’s thermal and performance metrics to ensure safe undervolting.
Examples of Undervolting Tools: Intel-undervolt, ThrottleStop, and Intel XTU. Other tools are also available and might be suitable depending on your specific needs.
Using software tools like Intel XTU or ThrottleStop for undervolting may affect your device's warranty. Always consult your device's warranty terms and the manufacturer's guidelines before proceeding.Note
Intel-undervolt
Intel-undervolt is specifically designed for undervolting Intel CPUs, particularly Haswell and newer models. It manipulates MSR and MCHBAR registers to achieve undervolting, while also enabling modifications to power and temperature limits. Notably, it isn’t compatible with Tiger Lake CPUs and beyond, but it does work with intel_pstate.
Installation and Configuration
Install the tool named intel-undervolt. Configure by editing the /etc/intel-undervolt.conf file. For example, an undervolt of -100mV to the CPU Cache can be set. Test Configuration: After saving the configuration file, use the tool to apply settings. A message of Success indicates the settings are applied correctly. For persistence, enable intel-undervolt.service.
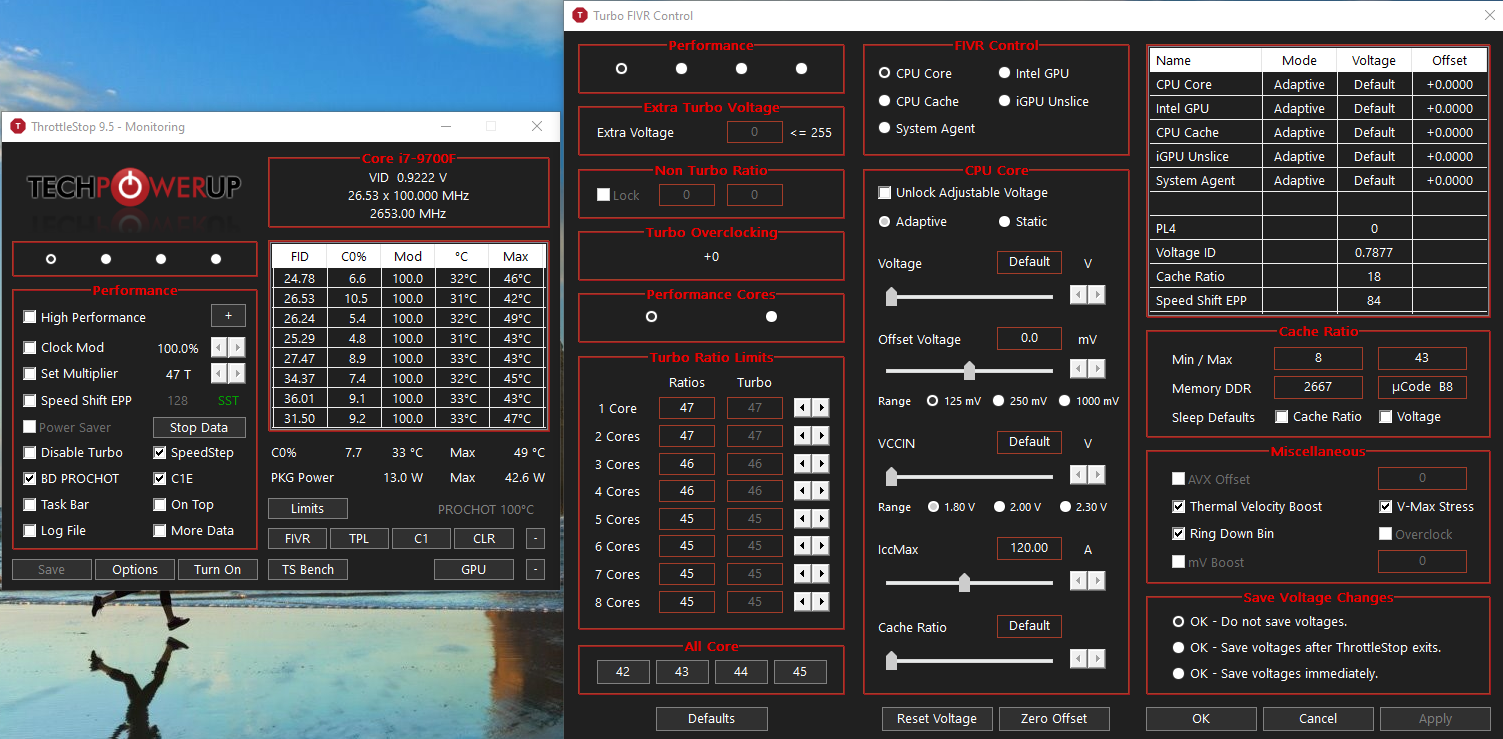
ThrottleStop
ThrottleStop is primarily designed for Intel processors. While it may theoretically work with AMD CPUs, its compatibility and effectiveness with AMD models are not guaranteed. It offers a user-friendly interface with numerous adjustable settings.
Setting Up ThrottleStop
- ThrottleStop can be obtained from reputable online sources.
- Run the program to see various options and processor information.
- Enable Speed Shift EPP for Intel processors to activate Speed Shift technology.
- Adjust Voltage: In the FIVR Control, enable Unlock Adjustable Voltage and set values for CPU Core, CPU Cache, and Intel GPU.
- Apply changes and monitor temperatures/voltages using a tool like HWMonitor.
- For laptops, set up profiles for AC and battery usage in ThrottleStop.
Intel XTU (Extreme Tuning Utility)
Intel XTU is a versatile tool suitable for both novice and experienced users. It offers a straightforward interface for undervolting and monitoring CPU behavior.
Using Intel XTU
- Intel XTU can be obtained from its official website or other reputable sources.
- Undervolt CPU: Adjust the voltage offset for the processor.
- Test Stability: Use benchmarks like Cinebench or Prime95 to ensure system stability.
Note: It is recommended to use the latest version of Intel XTU for enhanced features and to avoid profile incompatibility. Users with older versions of Intel XTU profiles (7.9 and older) could experience incompatibility, and would need to contact Intel Customer Support to convert older profiles. Once converted, these profiles can be used with the latest Intel XTU. Click here for more information.
Steps to Monitor and Adjust CPU Temperatures When Undervolting
- Select the Right Tools: Utilize software such as Intel XTU (Extreme Tuning Utility) for Intel CPUs or Ryzen Master for AMD CPUs. These tools allow for precise voltage adjustments and provide real-time monitoring of CPU temperatures and performance.
- Baseline Temperature and Performance Check: Before undervolting, record your CPU’s baseline temperature and performance. Run a stress test using applications like Prime95 or AIDA64 and note the temperatures and performance metrics using HWMonitor or a similar tool.
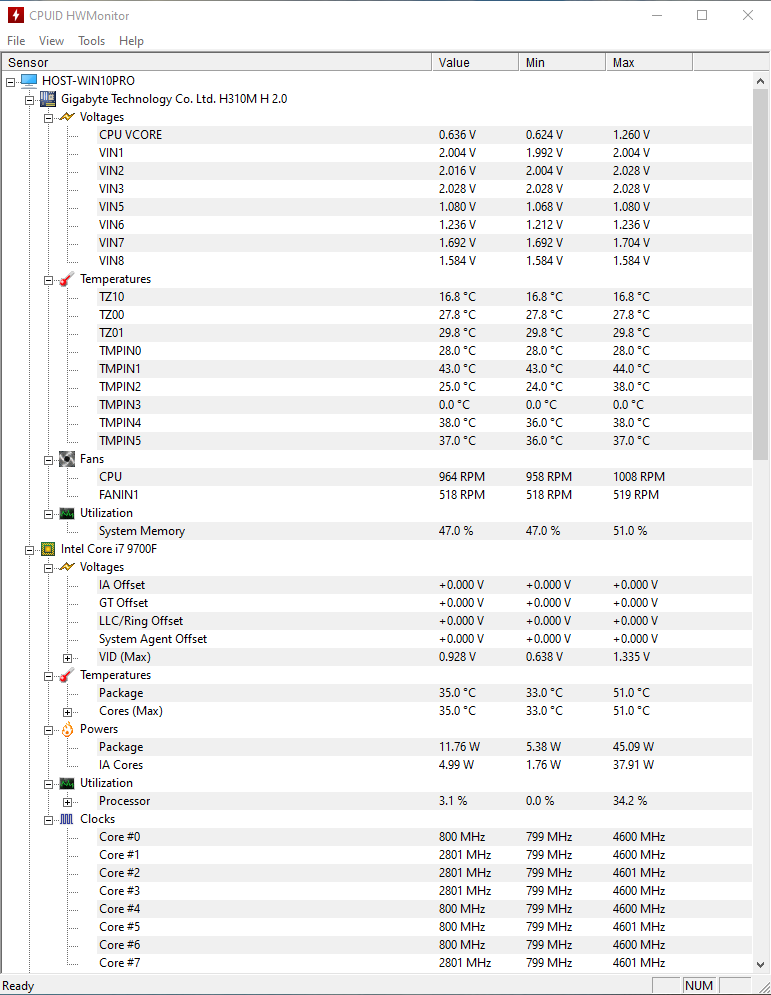
- Initial Undervolting: Reduce the CPU voltage incrementally. Start with a small decrease (e.g., -50mV) and gradually reduce further. Avoid significant voltage drops at the beginning to prevent system instability.
- Stress Testing: After each undervolt adjustment, perform a stress test. Monitor the CPU’s temperature and performance, ensuring there are no crashes, freezes, or significant performance drops.
- Finding the Sweet Spot: The goal is to find the optimal balance where the CPU operates cooler without sacrificing performance. This point varies for each CPU due to the silicon lottery. It’s achieved when the CPU is stable under load with reduced temperatures and no performance loss.
- Long-term Monitoring: Even after finding a stable undervolt setting, it’s important to continue monitoring the CPU over time, especially during different usage scenarios. This ensures that the undervolt is consistently stable.
- Community Insights: It’s helpful to look at online discussions where people share their experiences and tips about undervolting. This can give you practical advice and a better understanding of what to expect, provide a reference point and additional tips. For example, a discussion on Reddit’s r/Dell subreddit highlights significant temperature drops experienced by users when undervolting Dell laptops.
Advanced Considerations in Undervolting
- Adjusting Power and Temperature Limits: It’s like setting the right thermostat and power limits for your CPU so it works optimally without overheating or using too much energy.
- Understanding the Role of BIOS Settings: Some undervolting adjustments can be made directly in the BIOS, offering a more permanent solution compared to software tools.
Example Configurations from Online Discussions
- A user on the Linus Tech Tips forum reports improved performance and reduced heat by undervolting an Intel Core i7 CPU using a -100mV offset.
- Another experience shared on the Intel Community forum discusses the impact of undervolting an i9 13900K, emphasizing the need for continuous monitoring to ensure system stability.
Community Discussions
Engaging with online communities can provide valuable insights from others who have undertaken undervolting. Websites like Reddit, Linus Tech Tips forums, and Overclockers UK forums are excellent resources. Here’s a summary of community experiences:
- Many users report successful undervolting with temperature reductions of up to 10°C.
- Some have found that undervolting can lead to increased battery life in laptops.
- The community often emphasizes the importance of gradual adjustments and monitoring.
For more detailed user experiences, visit these discussions:
In conclusion, undervolting can be a powerful way to optimize your system, but it requires the right approach and tools. Careful monitoring and gradual adjustments are key to finding the ideal voltage setting for your hardware. Remember, every CPU and GPU is different, so what works for one might not work for another. Happy undervolting!
FAQ
Q: Is undervolting my laptop’s CPU safe?
A: Undervolting is generally safe, reducing CPU voltage to lower heat and energy consumption. However, it requires careful execution as incorrect settings can cause instability.
Q: Does undervolting a CPU decrease performance?
A: Undervolting usually maintains performance, reducing power and heat. It can potentially improve performance by preventing thermal throttling.
Q: What does undervolting a CPU do?
A: It reduces the CPU’s voltage, decreasing heat generation and power consumption, which can enhance CPU efficiency and longevity without impacting performance.
Q: What is the process of undervolting a CPU?
A: The process involves using software to incrementally lower the CPU’s voltage, monitoring for stability and performance to find the optimal voltage setting.
Q: What are the benefits and risks of undervolting a CPU?
A: Benefits include lower heat and power consumption, and potentially longer hardware lifespan. Risks include system instability, crashes, and possible hardware damage if done improperly.