When it comes to the power and performance of your computer, few things are as crucial as the speed of your central processing unit or CPU. But what exactly do we mean when we talk about CPU clock speed?
Clock speed, often referred to as clock rate or frequency, is essentially the heartbeat of your CPU. It’s expressed in gigahertz (GHz), which quantifies the number of cycles your processor executes every second. Each of these cycles represents a burst of activity during which your processor performs the calculations that power everything from simple word processing documents to complex video games.
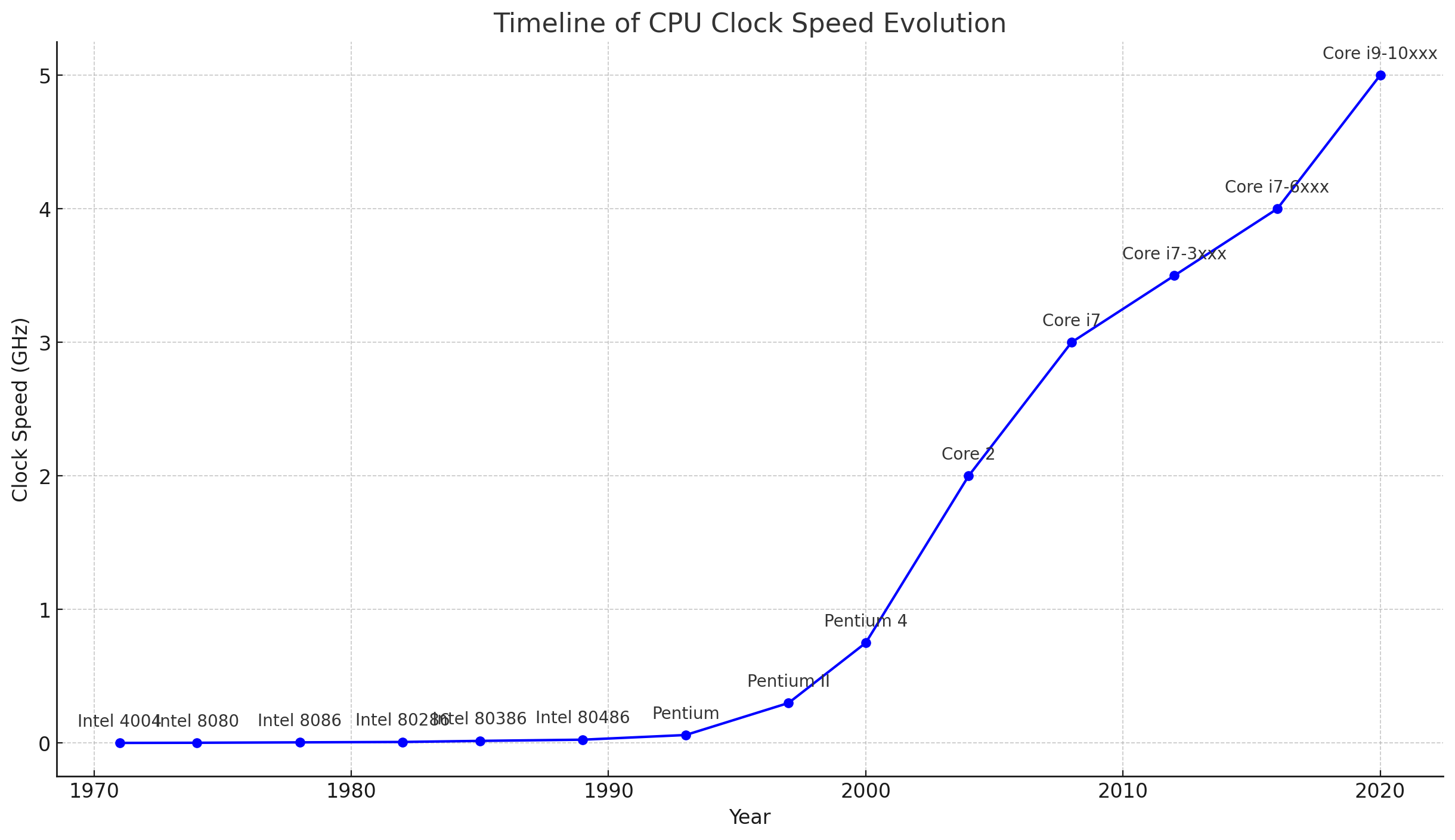
Timeline Graph of CPU Evolution
This timeline graph shows the evolution of CPU clock speeds over the years, including major technological milestones.
Imagine your CPU as an office filled with a diligent workforce, where each employee represents a transistor within the processor. Now, picture those employees opening and closing files, calculating figures, and executing tasks. The higher the clock speed, the faster they’re able to work, metaphorically speaking. For instance, a CPU with a speed of 3.2 GHz can execute 3.2 billion cycles per second, each cycle representing a potential operation performed by the CPU. It’s a bustling office where the pace is rapid and productivity is high.
But clock speed isn’t the only factor that determines performance. Newer CPUs may have lower clock speeds but can still outperform older models due to more efficient architectures, advanced features like dynamic frequency scaling, which adjusts the frequency based on the workload, and smarter core utilization, as seen in some modern processors. Consequently, a cutting-edge processor can handle more instructions more efficiently than its predecessors, translating into improved performance even with seemingly lower clock rates.
How to Check Your CPU Speed
To check your CPU’s clock speed:
- Windows: Open Task Manager, go to the ‘Performance’ tab to see real-time CPU speed. Alternatively, type “msinfo” in the Start Menu and look for CPU details under “Processor” in the System Information app.
- Mac: Click the Apple icon, select “About This Mac” to find CPU information.
- Linux: Linux: To find out how to check your CPU GHz or how to test CPU speed, utilize command line commands such as lscpu or inspect /proc/cpuinfo.
Intel processors list both a Processor Base Frequency and a Max Turbo Frequency, indicating performance levels for various tasks, including high-intensity activities like gaming.
How to Test CPU Speed through Overclocking
To overclock your CPU:
- Overclocking involves increasing the CPU’s clock speed beyond its base frequency for enhanced performance.
- Various tools offer user-friendly options for both beginners and experts to safely overclock their CPUs.
- Risks of overclocking include increased power demand and heat generation, which can shorten hardware lifespan or cause immediate damage if not well-managed.
- It’s crucial to use improved cooling solutions and consistently monitor the system during overclocking.
Explore the key advantages and disadvantages of CPU overclocking in this table, providing a succinct comparison for informed decision-making.
| Aspect | Pros of Overclocking | Cons of Overclocking |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Enhanced CPU speed and performance. Improved handling of demanding tasks and applications. |
Potential instability in system performance. May not yield significant performance improvements. |
| Cost-Efficiency | More performance from existing hardware, delaying the need for upgrades. Cost-effective for enthusiasts. |
Additional costs for cooling solutions and potential hardware replacements. |
| Customization | Personalized control over hardware capabilities. Satisfaction from DIY tweaking and optimization. |
Requires technical knowledge and time investment. Risk of incorrect settings leading to damage. |
| Thermal Management | Opportunity to learn about and improve cooling solutions. | Increased heat output can stress components. Need for advanced cooling systems. |
| Longevity | Can revitalize older hardware, extending its relevance. | Accelerated wear and tear, potentially reducing the lifespan of the CPU and other components. |
| Warranty and Support | Some manufacturers offer warranty support for overclocked systems. | Overclocking often voids manufacturer warranties. Lack of official support for issues related to overclocking. |
| Gaming and Workloads | Better gaming performance and faster processing in heavy workloads like video editing and rendering. | Diminishing returns for certain tasks; some applications may not benefit significantly from overclocking. |
| Stability | Opportunity to fine-tune system stability under controlled conditions. | Potential system crashes, freezes, and unpredictable behavior. |
| Energy Consumption | More performance per watt on older or lower-tier CPUs. | Increased power consumption leading to higher electricity bills. |
Comparing and Monitoring CPU Speed in Online Communities
Wondering how to tell what speed your CPU is running at or seeking advice on effective overclocking? Online forums and communities are bustling with discussions and advice. For example, websites like Ask Ubuntu serve as platforms where users share their experiences about checking CPU speeds and optimizing performance. Online communities and websites provide detailed benchmarks and analysis, helping users understand how clock speed affects gaming performance.
When delving into these resources, you might find technical debates, user recommendations for tools and tweaks, and insights into the latest hardware that can help inform your own system upgrades or overclocking strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding how to check your CPU GHz is crucial in computing performance, influencing task execution speed in activities like gaming, rendering, or browsing. While it’s important to know and manage your CPU’s frequency, remember that real-world performance also heavily depends on the CPU’s architecture and how it processes tasks. Clock speed is a key factor, but it’s part of a larger performance framework.
FAQ
Q: What is my CPU frequency and why is it important?
A: Your CPU frequency, measured in gigahertz (GHz), indicates how many cycles your processor completes per second. It’s a key factor in determining your computer’s performance, affecting everything from basic tasks to gaming and professional applications.
Q: How can I check my CPU speed on Windows?
A: To check CPU speed on Windows, open Task Manager and go to the ‘Performance’ tab. For a more detailed view, type “msinfo” in the Start Menu and look for CPU details under “Processor” in the System Information app.
Q: How do I see my CPU speed on a Mac?
A: On a Mac, click the Apple icon and select “About This Mac” to find detailed CPU information, including its speed.
Q: How can I tell what my CPU is clocked at in Linux?
A: In Linux, you can determine your CPU clock speed by using command line tools like “lscpu” or by checking the “/proc/cpuinfo” file for detailed CPU information.
Q: What does overclocking my CPU do?
A: Overclocking your CPU increases its clock speed beyond the factory setting, potentially enhancing performance for demanding tasks. However, it also comes with risks like increased heat and possible hardware damage.
Q: How can I test my CPU speed after overclocking?
A: After overclocking, you can test your CPU speed by using benchmarking tools or software that measure the frequency and performance under various loads.
